Prima Additive's Dedication to Additive Manufacturing and Environmental Sustainability
In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing, Additive Manufacturing (AM) has emerged as a beacon of innovation, reshaping traditional production paradigms with its ability to craft complex geometries and streamline waste management. Amidst this transformative wave stands Prima Additive, an Italian trailblazer dedicated to refining the art and science of metal additive manufacturing.
Prima Additive, a specialized company of the renowned Prima Industrie Group, boasts decades of experience in the realm of industrial machinery and laser systems. This rich heritage, combined with a relentless pursuit of innovation, positions Prima Additive as a trusted partner for businesses worldwide. Our expertise spans from metal 3D printing to laser welding, ensuring comprehensive solutions for diverse manufacturing needs.
However, as with any technological advancement, Additive Manufacturing presents its own set of challenges. One of the most pressing issues in this sector is the efficient and sustainable use of materials, particularly metal powders. Recognizing this, Prima Additive has placed a significant emphasis on material reuse, studying how to perform an effective Additive Manufacturing material recycling. With our efforts, we aim to address both the environmental and economic implications of material wastage.
Environmental sustainability is not just a buzzword for us; it's a commitment. The manufacturing sector, historically, has been a significant contributor to environmental degradation. However, with Additive Manufacturing, there's an opportunity to rewrite this narrative. By reusing and recycling metal powders, we can drastically reduce waste, minimize the carbon footprint, and promote a circular economy. This not only benefits the environment but also translates to cost savings for businesses, making it a win-win scenario.
Our dedication to sustainability is evident in our continuous research and development efforts. We invest heavily in understanding the intricacies of Additive Manufacturing metal powder reuse. This involves studying the properties of used metal powders, assessing their viability for reuse, and developing processes to ensure consistent quality. Our goal is to define standards that businesses can adopt to rely on recycled materials without compromising on the final product's integrity.
Furthermore, Prima Additive's commitment extends beyond just research. We actively collaborate with industry stakeholders, academic institutions, and research bodies to share knowledge and drive collective progress. By fostering such collaborations, we aim to accelerate the adoption of sustainable practices across the Additive Manufacturing sector. In the same way, we collaborate with metal powder manufacturers with the aim of providing our customers with increasingly high-performance materials.
The Factors Involved in the Reuse of Metal Powder
Additive Manufacturing has undeniably revolutionized the manufacturing landscape, offering unparalleled design freedom. However, as the technology matures, the industry faces the challenge of ensuring sustainable material usage. One of the most critical aspects of this sustainability drive is the concept of material reuse, particularly concerning metal powders.
As you already know, metal powders are the lifeblood of many Additive Manufacturing processes. Their quality, consistency, and properties directly influence the final product's performance. However, after each Additive Manufacturing cycle, not all metal powder is fused into the final product. A significant portion remains unfused and can be potentially reused. The question then arises: How many times can these metal powders be reused without compromising the product's quality?
Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF) process is highly sensitive to powder quality because it relies on creating precise and uniform powder beds for each layer of the build. The quality of the powder directly affects the layer thickness and density, which are critical for achieving the desired resolution and mechanical properties of the final component. Consequently, the recycling of powders in LPBF requires careful management to ensure that the powder remains within the specified particle size distribution and is free from contaminants that could affect melting behavior and part quality. For this, the sieving step is necessary to remove oversized particles and the practice of mixing with virgin powder to maintain consistent properties.
Direct Energy Deposition (DED), on the other hand, is more tolerant of variations in powder quality because the powder is fed directly into the melt pool created by the laser on the surface of the part. This process is less influenced by the issues of powder spreadability and uniform layering that are critical in Powder Bed Fusion. However, DED still requires paying due attention to powder fluidity and feed flow stability to ensure stable deposition rates and maintain high finished part quality. Recycling powders in Direct Energy Deposition might focus more on maintaining the chemical composition of the powder, as variations can have a significant impact on the mechanical properties and integrity of the final part.

Our research, starting from studies from reputable academic institutions all around the world, has delved deep into this question. The consensus is that metal powders, especially those like titanium and nickel alloys, can undergo multiple Additive Manufacturing cycles without significant degradation in their properties. This is a game-changer for the industry. By reusing metal powders, manufacturers can achieve substantial cost savings and reduce the environmental impact associated with mining and refining new materials.
However, the process is not limited to simply collecting and reusing unmelted powder. Several factors need consideration. For instance, the powder's particle size distribution can change after each cycle, potentially affecting the final product's properties. Moreover, contaminants can get introduced into the powder, necessitating thorough cleaning and sieving processes.
The benefits of metal powder reuse and recycling in Additive Manufacturing are manifold. From an environmental perspective, it promotes a circular economy, reducing the need for new raw materials and minimizing waste. Economically, it offers significant cost savings, especially when considering the high costs associated with some metal powders. Furthermore, by reducing the dependency on new material sources, manufacturers can achieve more consistent supply chains, insulating themselves from market volatility.
In summary, the future of Additive Manufacturing also depends on the ability of this technology to inspire and activate sustainable practices. Embracing metal powder reuse and recycling is not just an environmentally conscious decision but also a strategic one. As the industry continues to grow, manufacturers that adopt these sustainable practices will undoubtedly gain a strong competitive advantage over competitors.
Driving Industry-wide Change: Prima Additive's Machines and Sectoral Impact
In the realm of Additive Manufacturing, having reliable and efficient machines plays a pivotal role. At Prima Additive, we pride ourselves on offering a range of state-of-the-art machines tailored to meet diverse industrial needs, all while championing the cause of sustainability.
But our machines aren't just about performance; they're also about sustainability. As discussed in the previous sections, in fact, material reuse and recycling are critical for the future of Additive Manufacturing and thus our machines are designed with this in mind, ensuring optimal powder management, and facilitating efficient recycling processes.
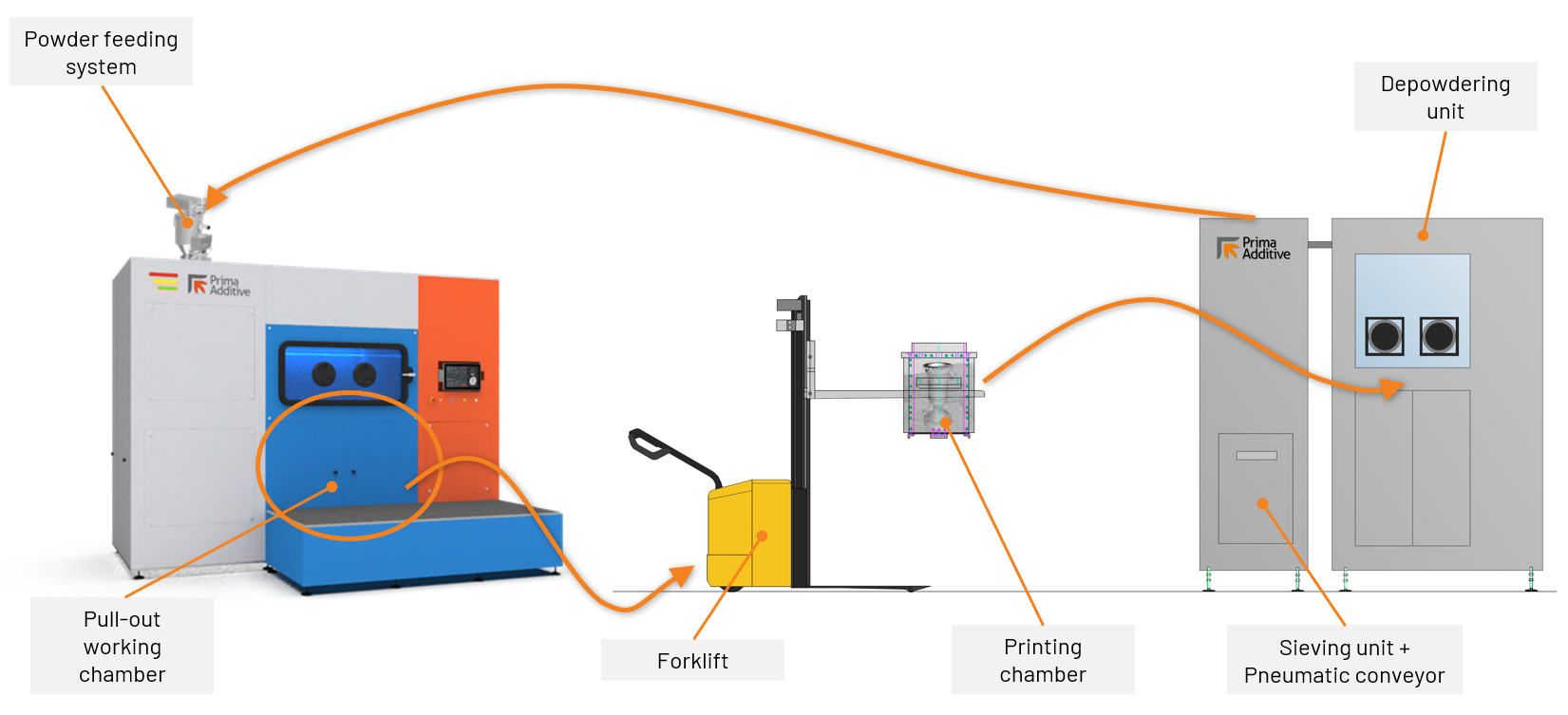
To be increasingly efficient in the use of powder, both in its management and in its reuse, we have developed functional solutions for the most automated management of powders possible. For example, on our 300 Family, there is an Automatic Powder Management System that allows you to automatically load and recycle unused powder directly into the machine. At the end of each job, it is possible to extract the working chamber from the machine and take it to the depowdering unit using a forklift. Inside the depowdering station, the unused powder is collected and sieved, and through the sieving unit connected to the machine via a pneumatic conveyor it is possible to automatically reintroduce the powder into the machine in a closed loop.
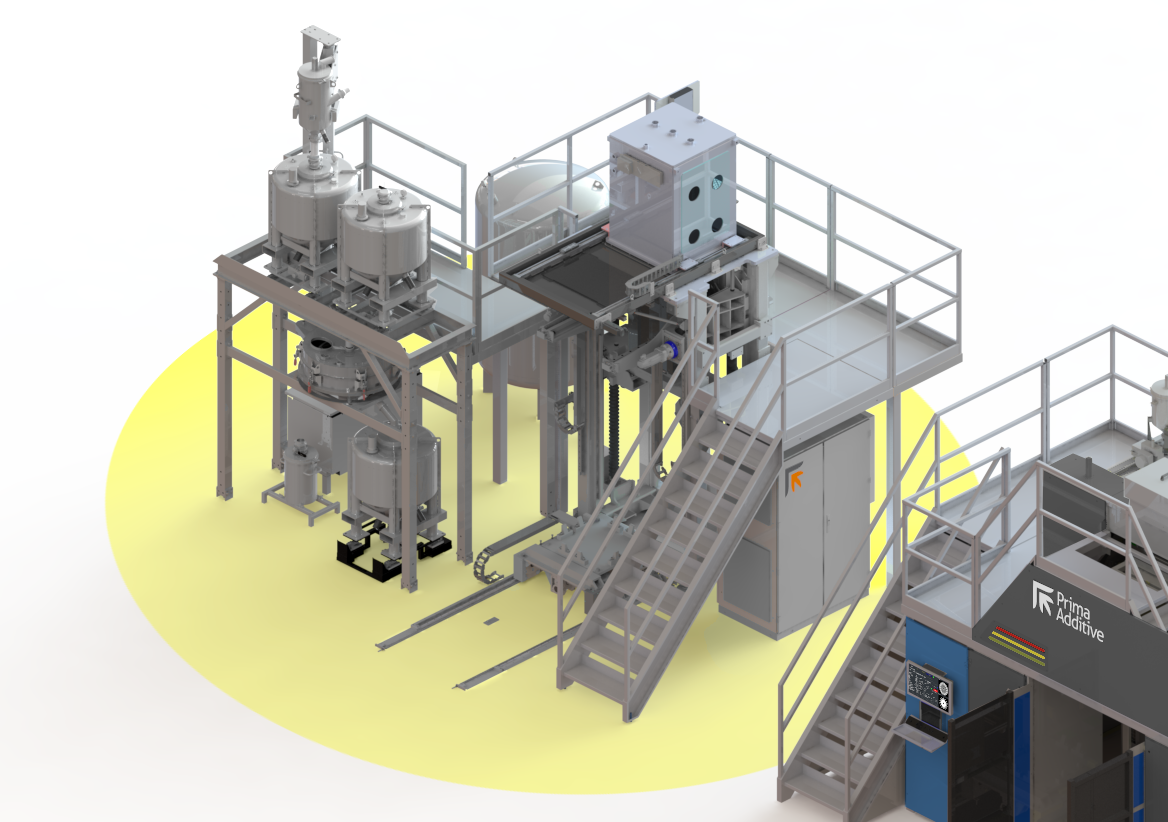
The same also happens in the case of larger machines, such as the 400 Family, which has an automatic powder management system, which after the depowdering stage allows the powder to be sieved and recycled, reintroducing it into the machine in a closed loop via an automatic powder feeding system. In cases like this, it is possible to scale operations, by connecting up to five machines to the same powder management system. Likewise, a system like this is crucial when it comes to managing recycled powder as it allows you to mix virgin powder and reused powder, adjusting the percentage of one and the other as needed.
Prima Additive's impact isn't limited to just providing machines. We actively engage with various industrial sectors, promoting the adoption of Additive Manufacturing and its sustainable practices. From aerospace to automotive, energy to medical, our machines cater to a wide array of applications. Each sector presents its own set of challenges, and our machines, backed by our extensive expertise, rise to the occasion, offering tailored solutions.
The same also happens in the case of larger machines, such as the 400 Family, which has an automatic powder management system, which after the depowdering stage allows the powder to be sieved and recycled, reintroducing it into the machine in a closed loop via an automatic powder feeding system. In cases like this, it is possible to scale operations, by connecting up to five machines to the same powder management system. Likewise, a system like this is crucial when it comes to managing recycled powder as it allows you to mix virgin powder and reused powder, adjusting the percentage of one and the other as needed.
Prima Additive's impact isn't limited to just providing machines. We actively engage with various industrial sectors, promoting the adoption of Additive Manufacturing and its sustainable practices. From aerospace to automotive, energy to medical, our machines cater to a wide array of applications. Each sector presents its own set of challenges, and our machines, backed by our extensive expertise, rise to the occasion, offering tailored solutions.
Beyond performance and sectoral applications, there's a broader vision that drives Prima Additive – a vision of a sustainable future. We believe that Additive Manufacturing has the potential to redefine manufacturing, making it more environmentally friendly and resource-efficient. By promoting material reuse and recycling, we're not just addressing the immediate challenges but also shaping the future of the industry.
Are you passionate about sustainability and looking to leverage the power of Additive Manufacturing? Contact Prima Additive today and explore how we can collaborate to make a lasting impact.